1. What is a thermoplastic?
Thermoplastics are a large class of plastics. They are made of thermoplastic resin and added with a certain proportion of auxiliary materials (such as various additives and fillers). The plastic can be softened or melted into any shape under certain temperature conditions, and the shape is unchanged after cooling. This state can be repeated many times and always has plasticity, and this repetition is only a physical change. The most widely used thermoplastics are: polyethylene PE, polypropylene PP, polyvinyl chloride PVC, polystyrene PS, aBS, polyamide (nylon) Pa, polycarbonate PC, and the like.
2. What is a thermosetting plastic?
Under certain temperature conditions, the plastic can soften into a molten state, and then harden and shape after cooling; however, if the hardened solid is heated and heated again, it cannot be melted and softened, indicating that the plastic is heated for the first time. At the time, chemical changes have taken place inside, calling this plastic a hot solid plastic. Commonly used thermosetting plastics are phenolic and epoxy resins.
Generally used in daily life, the handle of the pot, the power socket, the PC board, the pull switch, the plastic part on the knife switch, the plastic part of the electric iron, and the like.
3. What are the differences between thermoplastics and thermosets?
The simple difference is that the thermoplastic can be softened or melted by repeated heating to form a product; once the thermosetting plastic is molded, it cannot be softened, melted and reshaped even if heated. From the perspective of production methods: the thermoplastic molding process can be continuous, can be formed at high speed, and there are many process methods, and the defective products and waste plastics can be recycled and reused. The products have good mechanical properties, but the heat resistance and rigidity are poor. Thermosetting plastic molding can only be produced intermittently, it is difficult to achieve continuous production, and the production efficiency is low. In addition, thermosetting plastic products have higher heat resistance and pressure resistance than deformation of thermoplastic products.
4. What is general plastics and engineering plastics?
General purpose plastics and engineering plastics are a classification based on the scope and use of plastic products. General-purpose plastics are the most widely used plastic products with a wide range of production and ubiquitous life, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, phenolic resin and aminoplast. They are not only low in price, but also account for more than three-quarters of the total output of synthetic resins.
Engineering plastics are plastics that can replace some metal materials and are used to manufacture matching parts in various mechanical equipment. They have good mechanical properties and high long-term use temperature. Such plastics are polycarbonate, polyamide, polyoxymethylene, polysulfone, polyphenylene sulfide, polychloroether, and the like.
5. What kind of substance is plastic alloy?
The term "alloy" comes from metallurgy and refers to a new substance composed of a mixture of two or more metal chemical elements, which also has the characteristics of a metal material, which is called an alloy. "Plastic alloy" is the term borrowed from the metal alloy, which is used in polymer science. It is made up of two or more polymers, proportioned; blended under certain temperature and shear stress. . Whether by physical or chemical mixing, the formed multi-component polymer system is in a completely compatible state, forming a covalent bond at the interface, increasing the interface affinity and becoming a stable microphase separation state. In essence, this "plastic alloy" is a blend of polymers.
6. What is the glass, high elastic and viscous state of the polymer?
The glassy state, the high elastic state and the viscous state of the amorphous polymer refer to the relationship between the deformation state and the temperature change when a constant pressure is applied to the polymer. In the lower temperature environment, the polymer is in a rigid solid state, and has little deformation under the action of external force, similar to glass, so this state is called glass state. If the ambient temperature is raised to a certain temperature, the shape will change significantly under the action of external force. In a certain temperature zone, the morphological change is relatively stable. This state is called high elastic state. If the temperature continues to rise, the shape variable gradually increases with increasing temperature until it becomes a viscous fluid, at which point its shape cannot be recovered, and this state is a viscous flow state. Generally, the transition from a glass state to a high elastic state is called a glass transition, and the temperature range of the morphological transformation process is called a glass transition temperature; the high elastic state changes to a viscous flow state, and the temperature in the transition process section is called a viscous flow temperature.
7. What is high temperature resistant plastic?
High temperature resistant plastic refers to a plastic that has good high temperature resistance and can be applied in a temperature environment of more than 150 ° C. It is a plastic product with high price, small output and small application range. Such plastics are: silicone plastics, fluoroplastics, polyimides, polyphenylene sulfides, polydiphenyl ethers, and the like.
8. What is polymer plastic?
Many of the same molecular chains combine into a large molecule, and the chemical composition of the basic chemical composition does not change, called a polymer. This type of plastic is called a polymer plastic. Such as polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride and polymethyl methacrylate.
9. What is a condensate plastic?
When two or more different molecules are combined, water or other simple substances are released to form a chemical reactant completely different from the raw material molecule, called a condensate. This type of plastic is called a condensed plastic, such as a phenolic plastic. Amino plastics and silicone plastics.
10. What is pressure plastic?
A powder (or fibrous material) obtained by mixing a thermoplastic resin and a filler as a main raw material, and a variety of shapes prepared by compression molding is called a press plastic. For example, the pressed plastic with wood powder as the main filler is asbestos-based compression plastic and glass fiber-based compression plastic.
3phase motor Rebar Bending Machine is most popular in worldwide. Especially 3phase 380V 50Hz.
3phase rebar bending machine, resonable design, simple structure and can bend steel rod diameter to any required shape applying to bridge, tunnel and small, meduim as well as large construction projects.
1. Simple operation, safe and durable, high quality copper wire motor, guarantee a more stable performance.
2. Fully enclosed gearbox lubrication, worm gear and worm drive, with speed adjustable gear, strong bending strength, not rebound.
3. ultra-high hardened accessories, adjustable baffle which guarantee a longer service life.
4. Machine surface adopts plastic-spray treatment; Accessories like long strips and disc are solid, forged, and chrome plated, so they are beautiful and generous.
5. Specially use thickened steel plate, high rigid disc and bar iron, high power medium speed national standard high quality electronic motor, guarantee a more stable performance.
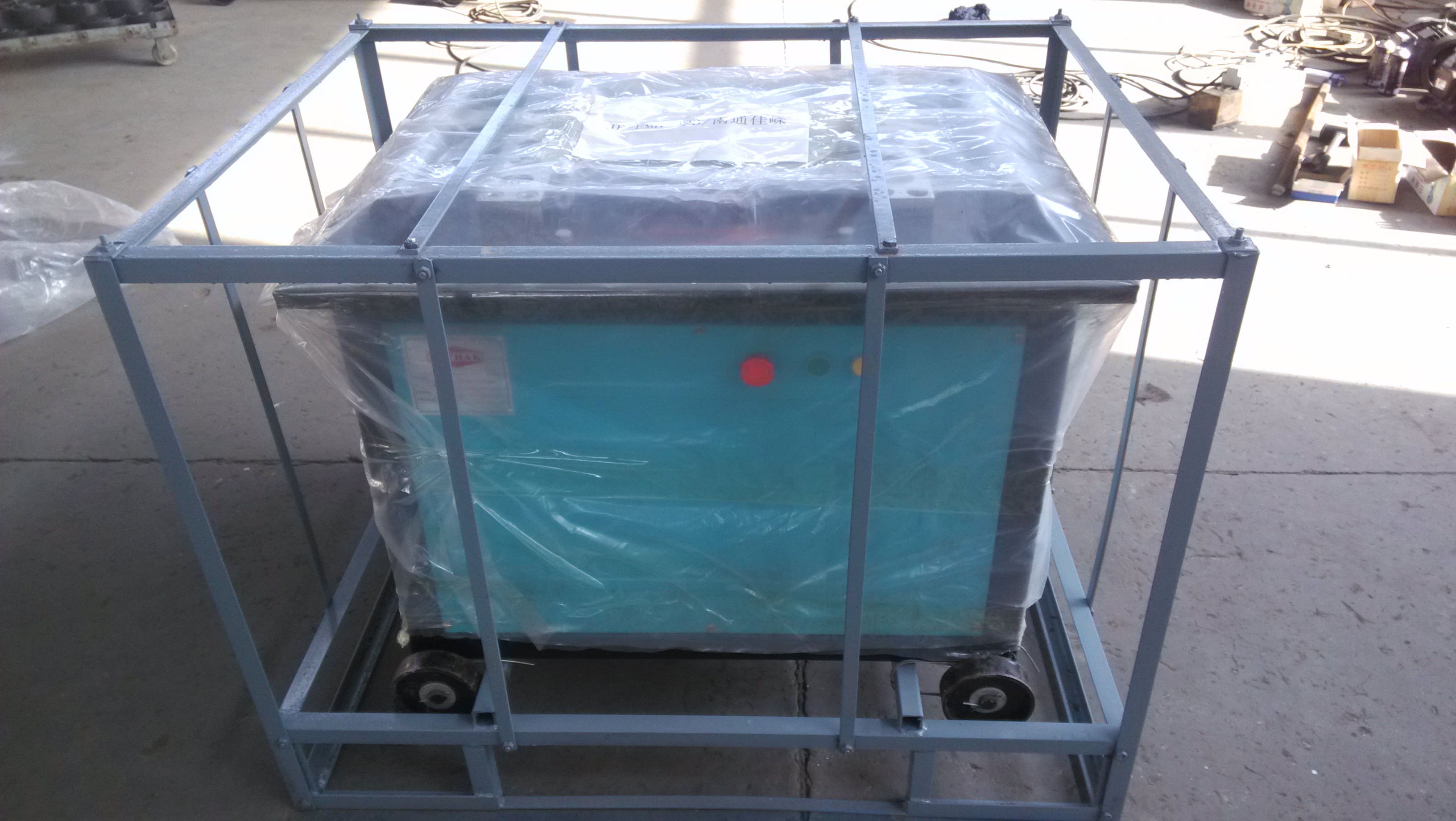


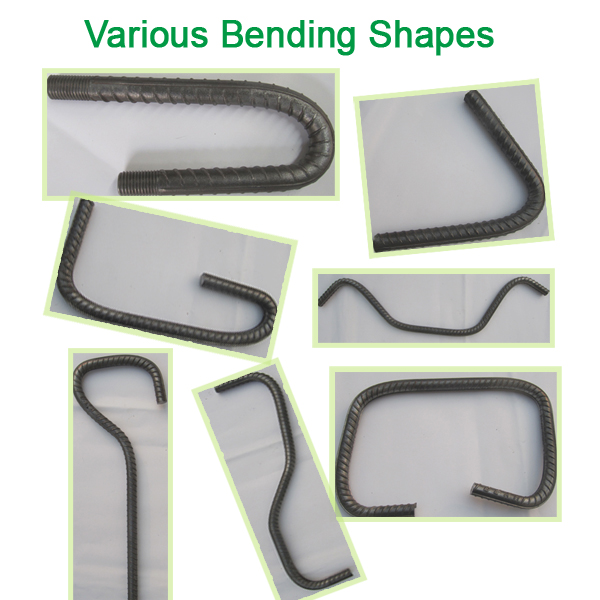

Steel Bar Rebar Bending Machine,Best Selling Rebar Bending Machine,Carbon Steel Rebar Bending Machine,Steel Rebar Bending Machine
BAODING JINDI MACHINERY CO., LTD , https://www.rebarconnector.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)