Common cutting fluids are used in casting, high-pressure cooling, and spray cooling. These methods help to cool the cutting zone, reduce friction, and improve tool life. Below are three commonly used techniques:
1. Pouring Method
The pouring method is the most widely used technique. It is simple to implement and commonly applied in many machining operations. However, it has some limitations. The flow rate is relatively low, and the pressure is not high enough to directly reach the maximum temperature area of the cutting edge, which can result in poor cooling and lubrication performance. To optimize this method, it's important to ensure a sufficient flow of fluid and position the pouring point as close to the cutting zone as possible. When using different types of tools, it's recommended to adjust the number and shape of the sprues according to the tool geometry and the number of cutting edges, as shown in Figure 1.
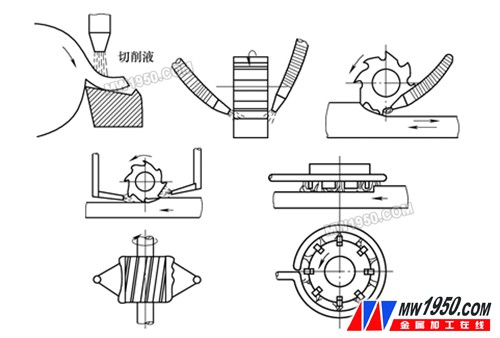
Figure 1: Cutting Fluid Pouring Method
2. High-Pressure Cooling Method
The high-pressure cooling method involves spraying cutting fluid at high pressure (1–10 MPa) and with a large flow rate (0.8–2.5 L/s) onto the cutting zone. This method is especially effective for deep hole machining, where the cutting fluid can directly reach the cutting area, providing efficient cooling and lubrication while also helping to flush out chips from the hole. It is also beneficial when machining difficult-to-cut materials with high-speed steel tools, significantly extending tool life. The cutting fluid can be either a general emulsion or a specialized cutting oil. Due to the high velocity of the fluid, its penetration into the cutting zone is improved, resulting in better cooling performance. However, one downside is that there is significant splashing, requiring proper shielding to protect the operator and surrounding equipment.
3. Spray Cooling Method
In the spray cooling method, the cutting fluid is atomized and sprayed onto the cutting zone using compressed air at 0.3–0.6 MPa. The high-speed airflow carries fine droplets of the fluid into the cutting area, where they rapidly evaporate due to the high temperature, absorbing a large amount of heat and providing excellent cooling. This technique is particularly suitable for machining difficult-to-cut materials, such as alloys and high-strength steels. However, it requires special spray devices and can be quite noisy during operation. As shown in Figure 2, the system typically includes an atomization unit and a nozzle assembly.
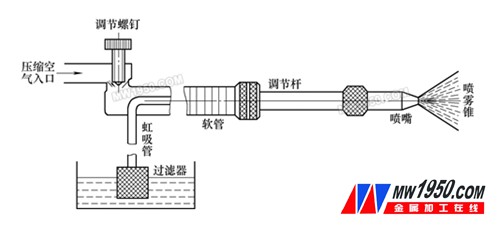
Figure 2: Spray Cooling Device Schematic
Colorful Led Light Doorbell,Led Colorful Light Doorbell,Color Light Doorbells,Doorbell Flashing Light
Foshan Shunde Advante Electron Ltd. , https://www.china-advante.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)